Crontab in Linux: EXAMPLES
Linux Crontab format
Crontab of Linux has six fields. The first five fields define the time and date of execution, and the 6’th field is used for command execution.
Crontab syntax:
[Minute] [hour] [Day_of_the_Month] [Month_of_the_Year] [Day_of_the_Week] [command]
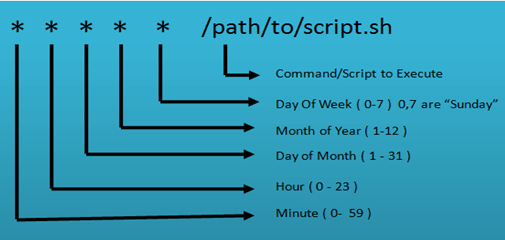
- Astrics (*): Use for matching
- Define range: Allows you to define a range with the help of hyphen like 1-10 or 30-40 or jan-mar, mon-wed.
- Define multiple ranges: Allows you to define various ranges with command separated like apr-jun,oct-dec.
How to Add/Modify Crontab
User can edit their crontab jobs with the help of following crontab command:
$ crontab -u -e
The above command will open the personal crontab configuration of your computer system, which can be edited by using your default text editor.
There is no need to restart your crontab as it will pick up your changes automatically when you use following command.
$ crontab -l
To remove your crontab tasks, use the following command.
$ crontab -r
To add or update job in crontab, use below given command.
crontab -e
Command to edit other user’s crontab
crontab -u username -e
How to List Crontab
Command to view crontab entries of current user
crontab -l
Command to view crontab entries of a specific user:
crontab -u username -l
Important Crontab Examples
Here, are some important examples of Crontab
| Description | Command |
|---|---|
| Cron command to do the various scheduling jobs. Below given command execute at 7 AM and 5 PM daily. | 0 7,17 * * * /scripts/script.sh |
| Command to execute a cron after every 5 minutes. | */5* * * * * /scripts/script.sh |
| Cron scheduler command helps you to execute the task on every Monday at 5 AM. This command is helpful for doing weekly tasks like system clean-up. | 0 5 * * mon /scripts/script.sh |
| Command run your script on 3 minutes interval. | */3 * * * * /scripts/monitor.sh |
| Command to schedule a cron to which executes for a specific month. This command to run tasks run in Feb, June and September months. Sometimes we need to schedule a task to execute a select monthly task. | * * * feb,jun,sep * /script/script.sh |
| Command to execute on selected days. This example will run each Monday and Wednesday at 5 PM. | 0 17 * * mon,wed /script/script.sh |
| This command allows cron to execute on first Saturday of every month. | 0 2 * * sat [ $(date +%d) -le 06 ] && /script/script.sh |
| Command to run a script for 6 hours interval so it can be configured like below. | 0 */6 * * * /scripts/script.sh |
| This command schedule a task to execute twice on Monday and Tuesday. Use the following settings to do it. | 0 4,17 * * mon,tue /scripts/script.sh |
| Command schedule a cron to execute after every 15 Seconds. | * * * * * /scripts/script.sh * * * * * sleep 15; /scripts/script.sh |
| Command to schedule tasks on a yearly basis. @yearly timestamp is= to “0 0 5 1 *”. This executes the task in the fifth minute of every year. You can use it to send for new year greetings. | @yearly /scripts/script.sh |
| Command tasks to execute on a monthly basis. @monthly timestamp is similar to “0 0 1 * *”. This command expression allows the execution of a task in the first minute of the month. | @monthly /scripts/script.sh |
| Command to execute multiple tasks using a single cron. | * * * * * /scripts/script.sh; /scripts/scrit2.sh |
| Command to schedule tasks to execute on a weekly basis. @weekly timestamp is similar to “0 0 4 * sun”. This is used to perform the weekly tasks like the system cleanup etc. | @weekly /bin/script.sh |
| Task will be scheduled to execute on a daily basis. @daily timestamp is similar to “0 2 * * *”. It executes the task in the second minute of every day. | @daily /scripts/script.sh |
| Allows tasks to execute on an hourly. @hourly timestamp is similar to “0 * * * *”. This command executes a task in the first minute of every hour. | @hourly /scripts/script.sh |
| Allows tasks to execute on system reboot. @reboot expression is useful for those tasks that the system wants to run on your system startup. This is helpful to begin tasks background automatically. | @reboot /scripts/script.sh |
Comments
Post a Comment